ProgrammingPro #52: .NET MAUI's Design Principles, Java's High Vulnerability, Streamlit Simplifies Data Apps, and GPT-4 Exploits Security Flaws
Bite-sized actionable content, practical tutorials, and resources for programmers
Welcome to this week’s edition of ProgrammingPro!
In today’s Expert Insight, we bring you an excerpt from the recently published book,
.NET MAUI Cross-Platform Application Development - Second Edition, which discusses the application of fundamental design principles, particularly SOLID principles, in software development.
News Highlights: Java services report 90% vulnerability rate; OpenSSF's new Protobom project aims to fortify software supply chain security; JetBrains launches comprehensive IDE Services for developer productivity; Rust updates to secure Windows deployments; and GPT-4 demonstrates high success in exploiting vulnerabilities, raising AI security concerns.
My top 5 picks from today’s learning resources:
But there’s more, so dive right in.
Stay Awesome!
Divya Anne Selvaraj
Editor-in-Chief
PS: If you have any food for thought, feedback, or would like us to find you a specific Programming learning resource for our next issue, take the survey. We will send you one Packt credit to buy a book of your choice as a thank you!
🗞️News and Analysis🔎
Java is the language that’s most prone to third-party vulnerabilities: Datadog's State of DevSecOps 2024 report has found that 90% of Java services harbor critical vulnerabilities, significantly higher than other programming languages. Read to learn more and understand the importance of thorough dependency checks.
OpenSSF, CISA, and DHS collaborate on new open-source project for creating
Software Bill of Materials (SBOMs): The project called Protobom is designed to simplify the creation, management, and interoperability of SBOMs across formats. Read for insights into the project’s impact on software supply chain security.
Security, automation and developer experience - The top DevOps trends of 2024: These trends are shaping new approaches to managing cloud governance, deployment processes, and developer support within organizations. Read to learn how these priorities can be implemented in your organization.
JetBrains aims to improve developer productivity with launch of IDE Services: The service integrates IDE Provisioner, AI Enterprise, License Vault, Code With Me Enterprise, and CodeCanvas, facilitating AI integration, pair programming, and much more. Read to learn how the service aims to enhance productivity.
Rust gets security fix for Windows vulnerability: The Rust programming language team has released Rust 1.77.2 to address a critical vulnerability specific to Windows deployments, identified as CVE-2024-24576. Read to learn how the update mitigates a critical vulnerability that could affect Windows users.
ECMAScript 2024 takes shape: The new update is set to introduce seven new features including array grouping, inspired by SQL's GROUP BY, and growable ArrayBuffers, which allow for dynamic memory management aligning with WebAssembly. Read to learn more.
Sourcegraph coding assistant now supports Anthropic Claude 3 – though limited to 7K token input: Cody now supports Anthropic's Claude 3 LLM, which offers better performance in code generation and a larger token context window compared to other models. Read to learn more about Cody’s updates.
OpenAI's GPT-4 can exploit real vulnerabilities by reading security advisories:
Researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign demonstrated that OpenAI's GPT-4 can effectively exploit real-world security vulnerabilities when given CVE advisories, achieving a success rate of 87%. Read to reflect on the significant questions this raises for the future of AI and security practices.
🎓Tutorials and Learning Resources💡
Python
🎓Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide to Python Logging Essentials: This article elucidates Python's logging module, detailing its components: records, handlers, formatters, and loggers. Read for illustrative code examples and insights for effective logging implementation.
🎓Tutorial | Pydantic - Simplifying Data Validation in Python: This tutorial introduces the library as a robust solution for data validation and settings management in Python, aimed at reducing boilerplate code and increasing code reliability. Read to learn how to apply Pydantic.
Intro to Streamlit - Web-based Python data apps made easy: Streamlit is a Python library that simplifies the creation of web-based data applications without needing HTML, CSS, or JavaScript knowledge. Read to learn how Streamlit enables the easy development of web-based Python data applications.
C# and .NET
🎓Tutorial | How to implement database connection resiliency in ASP.NET Core: This article takes you through setting up execution strategies that identify and handle transient errors without manual intervention. Read to learn how to enhance the stability and reliability of your ASP.NET Core.
🎓Tutorial | Data Anomaly Detection Using a Neural Autoencoder with C#: This article introduces the use of neural autoencoders in C# for data anomaly detection, illustrating a powerful but challenging method that requires fine-tuning multiple hyperparameters. Read to learn how to detect anomalies in data.
🎓Tutorial | Implementing Strategy Design Pattern in .NET: The Strategy Design Pattern, a part of the Gang of Four (GoF) patterns, encapsulates algorithms into separate classes, making them interchangeable and modifiable independently of the client code. Read to learn through concrete examples with different payment methods.
C and C++
Speculations on arenas and custom strings in C++: This article delves into the author's experimentation with arena allocation and custom strings in C++, highlighting the challenges and trade-offs involved. Read to learn about the practicalities and benefits of adapting C techniques to C++.
Cross compiling C/Rust to win32, again: In this detailed post, the author revisits cross-compiling C and Rust to win32, navigating through the challenges of missing compiler intrinsics and complex setup requirements. Read for inights into the nuances of different calling conventions, and the practicalities of inline assembly in programming languages.
Custom C++ Stream Manipulators: This article explains how to create custom stream manipulators in C++, offering functionality similar to built-in manipulators like std::endl. Read to learn techniques for extending C++ stream functionality to include custom behaviors.
Java
Strengthening Java Obfuscation with Native Code Integration: Traditional obfuscation in Java can be inadequate due to the detailed information retained in Java bytecode. Read to learn about a sophisticated method to enhance Java application security.
Understanding Heap Memory in Java Applications: This article explains Java memory management, focusing on heap memory, garbage collection, and JVM optimization for Java developers. Read to learn how to optimize garbage collection, and prevent common memory-related errors to enhance application performance.
🎓Tutorial | Comprehensive Guide to Unit Testing Spring AOP Aspects: This guide details testing strategies for various types of advice, the importance of isolating aspects, and using mocks for dependencies. Read to learn how to ensure aspects apply correctly across intended join points with robust, maintainable code.
JavaScript and TypeScript
🎓Tutorial | Full-stack web development with HTMX and Bun, Part 2 - Pug templating: Pug simplifies creating and managing HTML structures, which, combined with HTMX's capabilities, streamlines dynamic web applications. Read to learn how Pug complements HTMX and Bun in full-stack development.
ECMAScript 2024 features you can use now: ECMAScript 2024 will introduce four new features which are already supported in browsers and Node.js including Promise.withResolvers for enhanced control over promises. Read to learn how you can immediately incorporate these features into current JavaScript projects.
🎓Tutorial | How to build an in-memory Message Bus in TypeScript: This article explains message handling processes including sending, publishing, and scheduling with practical TypeScript interfaces and classes. Read to learn how to implement a message bus system in TypeScript.
Go
🎓Tutorial | Fundamentals of I/O in Go: Part Two: This article introduces advanced I/O operations in Go, featuring functions like io.LimitReader for restricting data read to a specific byte count. Read to learn how to effectively manage complex data flow scenarios in Go.
Go Is An Object Oriented Programming Language: The article argues that Go can be considered an OOP language because it supports encapsulation, polymorphism, and composition. Read to understand how Go's struct types, interface system, and inherent design encourage an OOP style.
Rust
Fivefold Slower Compared to Go? Optimizing Rust's Protobuf Decoding Performance: When optimizing GreptimeDB v0.7, it was found that its Protobuf deserialization for Prometheus write requests was substantially slower than a similar Go implementation. Read to learn how to optimize Rust's handling of byte arrays and memory management.
Trying Out Cloudflare's `foundations` Library for Rust: This article provides an in-depth review of Cloudflare's foundations library for Rust, highlighting its modular design and suitability for building networked services. Read to learn about foundations' comprehensive toolkit that supports a variety of backend needs.
PHP
Laravel Fundamentals - A Cheat Sheet for Rapid Development: This comprehensive guide to Laravel provides an in-depth look at its directory structure, basic Artisan commands, route types, middleware usage, and model relationships. Read to learn how to efficiently use Laravel for web development.
SQL
🎓Tutorial | The beauty of OLAP SQL: This article delves into using SQL for OLAP tasks, particularly for assessing product distribution and market competition in retail. Read to learn advanced SQL techniques for data analysis.
Ruby
🎓Tutorial | Abstract methods and NotImplementedError in Ruby: Ruby's NotImplementedError is often misused in abstract classes to enforce method implementation in subclasses, although it's actually intended for features not supported by the platform. Read to learn the appropriate use of NotImplementedError.
Swift
Swift for C++ Practitioners, Part 6: Error Handling: This article discusses error handling differences between C++ and Swift, focusing on Swift's method of handling errors, which contrasts with C++'s traditional approaches. Read to learn about Swift's effective error handling model that enhances code safety and maintainability.
Kotlin
Using Kotlin Multiplatform with KMMBridge and SKIE to publish a native Swift SDK: This article discusses leveraging KMP, SKIE, and KMMBridge to streamline Swift SDK development. Read to learn how you can balance benefits like reduced code maintenance with challenges such as configuration intricacies.
🌟Best Practices, Advice, and Case Studies🚀
What is Semantic Kernel?: This article introduces Semantic Kernel, an open-source SDK for building AI agents that integrate existing code with AI models. Read to learn how to use and extend Semantic Kernel for your AI projects.
Game On For Secure Coding - Gamifying The DevSecOps Lifecycle: This article discusses how gamification can enhance DevSecOps by motivating teams to adopt security practices through interactive challenges, visualized metrics, and rewards. Read for insights into creating a dynamic and rewarding work environment focused on security.
A Developer's Guide to Database Sharding With MongoDB: Database sharding enhances performance by distributing data across multiple servers. Read to learn about its benefits, different sharding strategies, and how to implement sharding in MongoDB to improve application performance and scalability.
Boosting Developer Productivity - Tools and Techniques for Efficient Coding: This article emphasizes the importance of deep focus and efficient coding techniques. Read to learn about strategies including optimizing IDEs, clarifying project specifications, reducing unnecessary tests, and utilizing no-code platforms.
🧠 Expert Insight 📚
Here’s an exclusive excerpt from “Chapter 6: Software Design with Dependency Injection” in the book, .NET MAUI Cross-Platform Application Development - Second Edition by Roger Ye.
A brief overview of design principles
Design principles are high-level guidelines that offer valuable advice on design considerations. These principles can provide essential guidance to help you make better design decisions. Some
general design principles are applicable not only to software design but also to other design disciplines.
Let’s review some general design principles before we explore the commonly used design principles (SOLID) in software development.
Exploring types of design principles
Design principles encompass a vast subject area. Thus, rather than delving into intricate details, I will provide insights from my experiences in implementing design principles during development, offering a concise overview of the principles discussed in this book. We will begin with high-level principles such as DRY, KISS, and YAGNI, and then progress to those more commonly used in software development. In the realm of object-oriented programming (OOP), the most widely used design principles are the SOLID principles.
Don’t Repeat Yourself (DRY)
As people often say, don’t reinvent the wheel; we should strive to reuse existing components instead of redeveloping what has already been created.
Keep It Simple, Stupid (KISS)
We should choose a simple and straightforward approach rather than involve unnecessary complexity in a design.
You Aren’t Gonna Need It (YAGNI)
We should implement functionality when it is required. In software development, there is a tendency to futureproof a design. This may create something that is actually not needed and increase the complexity of the solution.
SOLID design principles
SOLID design principles are widely employed in software development and serve as high-level guidelines for numerous design patterns. SOLID is an acronym that encapsulates the following five principles:
Single Responsibility Principle (SRP): A class should have a single responsibility. Adhering to this design principle, a developer should have only one reason to modify a class. By considering this principle during implementation, the resulting code becomes easier to comprehend and more effectively adapts to evolving requirements.
Open/Closed Principle (OCP): Classes should be open for extension but closed for modification. The central concept behind this principle is to prevent disruptions to existing code when introducing new features.
Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP): If the object of the parent type can be used in a context, an object with a child type should also be able to function in the same manner without causing any errors or disruptions.
Interface Segregation Principle (ISP): A design should not implement an interface that it doesn’t use, and a class should not be forced to depend on methods it doesn’t intend to implement. We should design concise and simple interfaces rather than large and complex ones.
Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP): This principle emphasizes the decoupling of software modules. High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules directly. Both should depend on abstractions. Abstractions should not depend on details. Details should depend on abstractions.
Design principles are guidelines to help us to make better design decisions. However, the responsibility ultimately lies with us to determine the most suitable course of action during the actual implementation, rather than solely relying on these principles.
Since we will focus on the usage of DI in this chapter, please refer to the Further reading section to find more information about design principles (SOLID) and design patterns.
Using design principles
Having discussed various design principles, allow me to share insights and lessons learned from implementing them in practice.
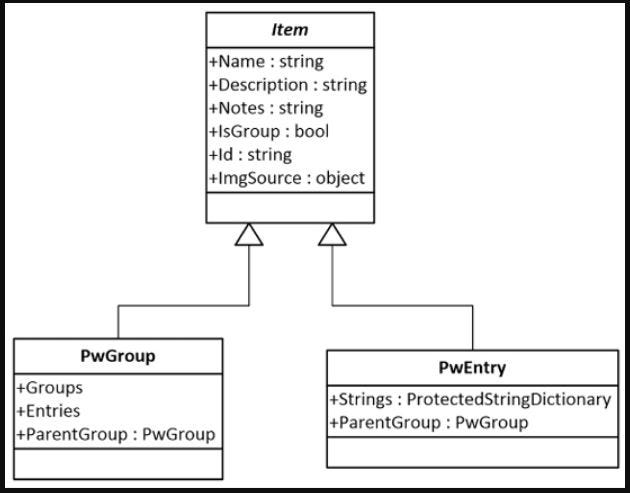
In our app’s model (the app we are building in this book), I utilized the KeePassLib from Dominik Reichl. While porting it to .NET Standard, I modified the inheritance hierarchy, as depicted in Figure 6.1:
Figure 6.1: Class diagram of Item, PwEntry, and PwGroup
In the process of porting KeePassLib to .NET Standard, I developed an abstract parent class, Item, for the group (PwGroup) and entry (PwEntry). This modification appears to violate OCP within the SOLID principles. The rationale behind this approach is rooted in a lesson I learned from the past implementation.
In earlier versions, prior to 1.2.3, I had not implemented KPCLib in the manner described. Instead, I directly used PwGroup and PwEntry, which required handling groups and entries separately. This resulted in increased complexity in ItemsPage and ItemsViewModel. This approach’s most significant consequence was the inability to distinctly separate the model and the view model. Consequently, I had to manage numerous details using KeePassLib directly within the view model. However, upon introducing the Item abstract parent class, I successfully concealed most of the intricate implementation within services (IDataStore and IUserService) and PassXYZLib. This led to the elimination of any code reliant on KeePassLib within the view and view model.
The inspiration behind this change came from the KISS principle rather than merely adhering to OCP. When considering other SOLID principles, such as LSP and SRP, this modification significantly improved the overall architecture. It’s essential to recognize that, in practical work, conflicts can arise among various design principles. It is ultimately our responsibility to make informed decisions instead of adhering dogmatically to design principles. The most effective design decisions typically arise from the insights gained from prior failures.
Returning to our main focus, we will now discuss enhancing the design by employing one of the SOLID principles—dependency inversion. As part of the SOLID design principles, dependency inversion emphasizes the separation of software modules, and it also provides guidelines on how to achieve this. The fundamental concept behind it is the preference of relying on abstractions whenever possible. In practice, DI is a technique routinely used to implement the idea of dependency inversion.
Packt library subscribers can continue reading the chapter for free here. .NET MAUI Cross-Platform Application Development - Second Edition by Roger Ye was published in March 2024. You buy the book here!
🛠️ Useful Tools ⚒️
Edera: an open-source project that boosts container security through a Rust-based runtime on the Xen hypervisor, providing strong isolation and protection against vulnerabilities.
Apache Airflow: a tool for scheduling and automating complex workflows, ranging from simple scripts to extensive data operations across multiple sources.
unpack: a tool for managing Python package dependencies, identifying usage status, analyzing disk usage, and understanding package relationships in projects.
That’s all for today.
We have an entire range of newsletters with focused content for tech pros. Subscribe to the ones you find the most useful here. Complete ProgrammingPro archives can be found here. Complete PythonPro archives are here.
If your company is interested in reaching an audience of developers, software engineers, and tech decision makers, you may want to advertise with us.
If you have any feedback, leave a comment below.